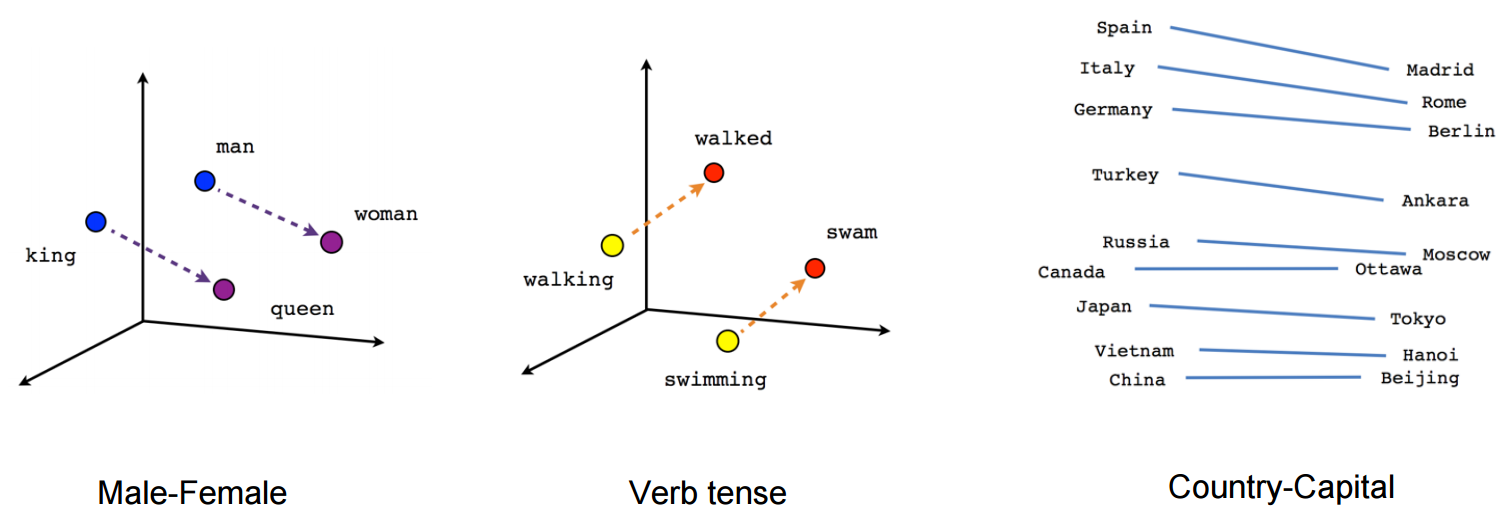
The EM algorithm for word alignment in SMT. Beam search for decoding. Introduction to neural machine translation: the encoder-decoder neural architecture; back translation; byte pair encoding. The BLEU evaluation score. Performances and recent improvements. End of the course!